Osteoarthrosis (deforming arthrosis, people's names - the accumulation of salts) - a chronic disease of the joints degenerative-dystrophic character, in which there is destruction of the articular cartilage, the joint capsule, deformation of the bone use.
It should be noted that osteoarthritis is a group of diseases of the joints, with different origins and close mechanisms of development. The most common arthritis of the large joints:
- deforming arthrosis of the knee joint (gonarthrosis),
- deforming arthrosis of the hip joint (coxarthrosis),
- and also osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint.
This is the most likely to have a serious types of arthritis.
Osteoarthritis of the small joints are rare. Common deforming osteoarthritis of the fingers of the hands, joints, and metacarpal-phalangeal major joints of the fingers of the Hand. Patients report pain in the interphalangeal joints, reduction in mobility, the appearance of the vicinity of the joints, seals (nodules Heberdena and Bouchard). This type of arthritis are more common in older people. Not infrequently, there is the arthrosis of the joints of the foot.
The polyarth roses, the generalized pattern, or osteoarthritis, characterized by lesions of multiple joints.
Osteoarthritis of the vertebral joints, spondylarthritis refers to a group of diseases of the spine, although it is similar to the other Mechanisms of the development of osteoarthritis.
The main clinical Symptom of osteoarthritis is pain in the joint, reducing your mobility. The specific symptoms are determined by the stage of the osteoarthritis and, depending on the extent of the destructive changes in the joint.
Causes of osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis are divided into primary and secondary. Primary (idiopathic) osteoarthritis is the result of the violation and the strengthening of the regenerative processes in the Degeneration of cartilage joint tissue without any abnormalities in the working of the whole organism. The secondary osteoarthritis is the result of other pathological processes in the body, either in the already damaged some of the outer joint influences, in the event of a partial destruction of the articular surfaces.
Usually traumatic osteoarthritis in younger patients diagnosed. And in patients of higher age is not always possible to draw a clear line between primary and secondary osteoarthritis.
Although the exact cause of the osteoarthritis is not possible to determine factors affecting the emergence and development.
You can the following types of reasons, which deform to the development of primary and secondary osteoarthritis.
The causes of the primary osteoarthritis hereditary factors
The following hereditary diseases that can lead to resulted in the development of primary osteoarthritis:
- genetic disorders in the composition of the cartilage of the joint, the accelerated destruction;
- congenital defects of the musculoskeletal system (joint hypermobility, dysplasia, flat feet, and other) as the reason for the trauma of the individual sections of the cartilaginous tissue of the joint, and, as a consequence, the emergence of osteoarthritis.
It was also noted that the degenerative joints osteoarthritis of the fingers of the upper extremities, occurs predominantly in women and is by inheritance in the female line.
Causes of secondary osteoarthritis
Secondary osteoarthritis is a result of the damage to the joint. This damage can by a variety of factors.
- Mechanical damage to the joints. To this group are among the various factors joint injuries, intraarticular fractures of the bone, in consequence of disturbances in the structure of the joint. The same result is a constant micro-fracturing joints due to excessive constant loads, such as static, as well as dynamically (e.g., in athletes). Also leads to overloading and trauma to the joints, obesity.
Another factor that has a significant negative impact on the joints (especially the hip), weakness of an attitude.
The structure of the joint can also surgery interfere. - Diseases of the joints. Osteoarthritis can develop as a result of inflammatory diseases of the joints (acute and chronic Arthritis, Synovitis, primary aseptic necrosis of the bone tissue, etc.)
- Metabolic disorders, diseases of the endocrine system, the chard of minerals in the body. Various disturbances of metabolism, a chard of Calcium, phosphorus and other minerals, vitamins and trace elements lead to changes in the composition of the bone, the benefits and the cartilage, synovial fluid, leading to a violation of the recovery processes, and the gradual destruction of the stock.
- Autoimmune diseases (gout, chondro calcinosis, hemochromatosis, Psoriasis, rheumatoid Arthritis), disorders of the hormone balance, estrogen deficiency in postmenopausal women can lead to changes in the tissues of the joints and their progressive destruction.
- Vascular disease (atherosclerosis of the vessels of the lower limb, arterial occlusive disease, leg ulcers), as well as lack of exercise cause disorders of blood circulation in periarticular tissues, poor blood supply to the tissues of the joint and subsequent degenerative changes.
The Mechanisms of the development of osteoarthritis
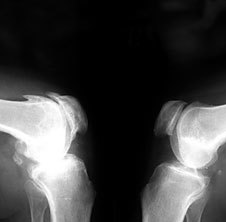
The development of osteoarthritis begins with the destruction of the cartilage. It is assumed that at the beginning of circulatory disorders in the capillaries Podhradie layer of the periosteum. Since the nutrition of the cartilage is effected by the supply of nutrients from the synovial fluid and the adjacent bone tissue, the poor circulation causes the cartilage gradually loses its elasticity, becomes thinner, the cracks, the smoothness of the articular surfaces is disturbed, decreases the amount of synovial fluid, which glide in the joint. The result is a pain and a crunching motion. Width of joint gap gradually decreases at the edges of the articular surfaces and form bony spikes-osteophytes.
Finally, the joint is deformed, the Amplitude of the movements in it reduces. Thus, involutive osteoarthritis, associated with the aging of the organism develops. The development of this Form of arthritis usually occurs gradually, over the course of many years.
Other forms of Arthritis of the large joints, such as post-traumatic, post-infectious, metabolic, substance-induced have several other mechanisms of development, but as a result, we get similar changes in the joint.
Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the joints. Stage and extent of the arthrosis
"Classic" as a classification of the osteoarthritis on the basis of clinical and radiological signs. In accordance with her, there are three stages in the development of the disease. It corresponds to the classification according to the degree of preservation of working capacity, single grade 3 osteoarthritis:
- I degree of osteoarthritis - disease does not prevent the implementation of the work, although it is difficult to find it,
- (II) the extent of the osteoarthritis disease prevents the execution of the work,
- (III) the degree of osteoarthritis - loss of ability to work.
We look at the clinical symptoms and signs of osteoarthritis on each of the stages referred to
Osteoarthritis of 1 degree (the initial stage of arthrosis)
In the early stages of the disease, in the morning, after a Pause, celebrated stiffness, difficulty of movement in the joints, and the plays some time after the beginning of the movement. Maybe a restriction of the mobility in the joint. In regular intervals there are "starter" pain (pain when starting after a prolonged stay in a state of rest). In the case of sharp movements Joint crackles, but not in pain at the movement. Pain in this stage of the osteoarthritis is only subsides in a substantial and permanent burden, and to rest. At rest and during low loads, no pain. In this stage of the disease the patients rarely by a doctor to be treated.
On the x-ray for osteoarthritis of 1 degree specific changes in the joint is not visible, can sometimes be visible small osteophytes on the edges of the joint, arthritic gap a little narrowed.
Osteoarthritis 2 grade (the second stage of arthrosis)
In the further development of osteoarthritis, the pain is greater, wins in sharp focus. A crunch in the joint, appears in all of the movements, observed a significant restriction of mobility in the joint (contracture), the functional shortening of the limbs, disorders of the biomechanics of the movements, but the mobility of the joint is still saved. At this stage, a considerable amplification of the initial pain, they are sharp and longer. Under the influence of daily physical load is constant fatigue appears joints, a feeling of pressure in the affected, the result is the so-called "mechanical pain", caused by reduced amortization of skills cartilaginous tissue of the joint.
To deform the destruction in the joint is already quite significant, joints start part already.
On radiographs, significant osteophytes, joint space narrowing, 2-3 times in comparison with the Norm, observed sclerosis of the subchondral bone and the formation of cystic cavities in the epiphyses Zone.
Osteoarthritis 2 degree by a decrease in the ability to work, the inability to perform certain types of work.
Osteoarthritis grade 3 (the third stage of osteoarthritis)
Osteoarthritis 3 degrees - it's hard, started, stage of the disease. In this Phase, observed:
- a significant deformity of the joint (due to the Proliferation of bone use, and the accumulation of fluid in the joint cavity);
- drastic limitation of movement, until the only store vibration movements;
- sharp pain not only when driving but also in a state of complete tranquility - constant pain associated with Reflex spasm of the surrounding muscles, as well as the development of reactive Synovitis;
- Inflammation of the joints,
- the sensitivity of the joints of the weather.
- the muscles around the king's meadow spasmatic and stunted;
The axis of the extremities deformed, clearly varus or valgus curvature of the foot (i.e. in the Form of the letter "O" or "X").
On the x-ray imaging in osteoarthritis 3 degree, there is an almost complete disappearance of the joint pan for cracks, severe deformation of the articular surfaces, wide multiple Boundary osteophytes. Determined joint-mouse and calcification, para-articular tissue can be.
In 3 the extent of the disease is very far, often it is the cause of the disability. Is expressed as follows:
- the pain will migrate to the constant and tormenting: and, above all, and climbing stairs descent - an ordeal for the patient;
- a loud crunch with every movement, well-audible to others;
- Deformation of the joints is strongly pronounced movements are only a small Amplitude, or even impossible;
To see the pictures of the destruction of the intra-articular structures (ligaments and menisci), as well as the complete abrasion of the cartilage and signs of sclerosis (a substitute for functioning institutions and structures, connective tissue) is.
Osteoarthritis 4 Grade
The state of the complete destruction of the joint in osteoarthritisif the joint is not functioning completely often emit in a separate - 4 degrees of osteoarthritis. There are the so-called "Blockade of the joint" - acute pain syndrome, even impossible for a limited movement in the affected joint. The fourth degree of osteoarthritis is correlated accompanied by pain in the joints is unbearable, even with strong painkillers, and Intensive physical therapy. Possible complete ankylosis (fusion of joint) or newartriot (formation of a false joint between the displaced ends of the bone to use). Independent movement in both cases is practically impossible.
In the pictures the rough sclerosis soslanovna surfaces is visible in the gap with a strong kistoznymi the enlightenment, the accretion of connecting bone to use in the area of the joint. The development of the disease up to this point almost always means the disability, to prevent the only of the prosthesis, Implantation of an artificial joint.
The treatment of osteoarthritis
The treatment of osteoarthritis in the early stages of the disease
Start osteoarthritis would be better to treat as early as possible, at the first signs of a Crunch in the joints, difficulty in movement. In this Phase, helpful drugs - chondroprotectors, the structure of the cartilage, and Vitamin-Mineral complexes.
The significance of the movement therapy, the right nutrition as well as preventive measures. It should be noted that the prevention of osteoarthritis is of great importance, and to prevent the exacerbation of the disease.
The treatment of osteoarthritis 2 - 3 degrees
Although to completely cure osteoarthritis 2-3 degree no longer possible, but the process of its development will be slowed down considerably. Treatment for osteoarthritis in this stage includes the following steps:
- remove or reduce the pain syndrome
- you remove the inflammation in the joint.
- improve the recovery of the cartilage and delay the degenerative processes in your.
In the acute Phase of treatment of osteoarthritis begins with the removal of the pain. This hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), analgesics not be. Possible intra-articular corticosteroid injections. Reduce the load on the joint, can't walk long or stand, lift heavy objects.
After the elimination of acute pain syndrome the main task is to ensure, as far as is possible, to the activation of regenerative processes in the joint and periarticular tissues: improvement in blood circulation, increased metabolism, elimination of inflammatory processes. Chondroprotectors, vasodilators as well as physiotherapy and physiotherapy appointed.
The treatment of osteoarthritis grade 4
At this stage, the joints are already destroyed almost completely. In this case, an output Operation and replacement of the affected joint endoprosthesis remains. Endoprosthesis improves the mobility of the joint, allowing the patient an active way of life, as a Minimum, get rid of the pain.














































